In the realm of gardening and horticulture, the battle against diseases and pests is an ongoing challenge. One such fungal disease that frequently plagues plants is Ghost Spot, scientifically known as Botrytis. Named after the pale, ghostly blotches it leaves on plant leaves and stems, this highly contagious disease poses a significant threat to various plants, including vegetables, fruit trees, flowers, and ornamental plants.
Ghost Spot, with its distinctive appearance and tendency to spread rapidly, requires swift intervention and preventive measures to protect the vibrant beauty and productivity of our gardens. Understanding this fungal disease, its mode of transmission, symptoms, prevention, and treatment methods is vital for gardeners seeking to combat and control Ghost Spot effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the world of Ghost Spot, exploring its characteristics and impact on plants. We will discuss the various ways it spreads and the symptoms that gardeners should watch out for. Furthermore, we will provide valuable insights on preventative strategies and treatment options to minimize the damage caused by this pervasive fungal disease.
Join us as we shed light on Ghost Spot, equipping gardeners with the knowledge and tools necessary to safeguard their cherished plants and create thriving, disease-resistant gardens.
What is Ghost Spot?
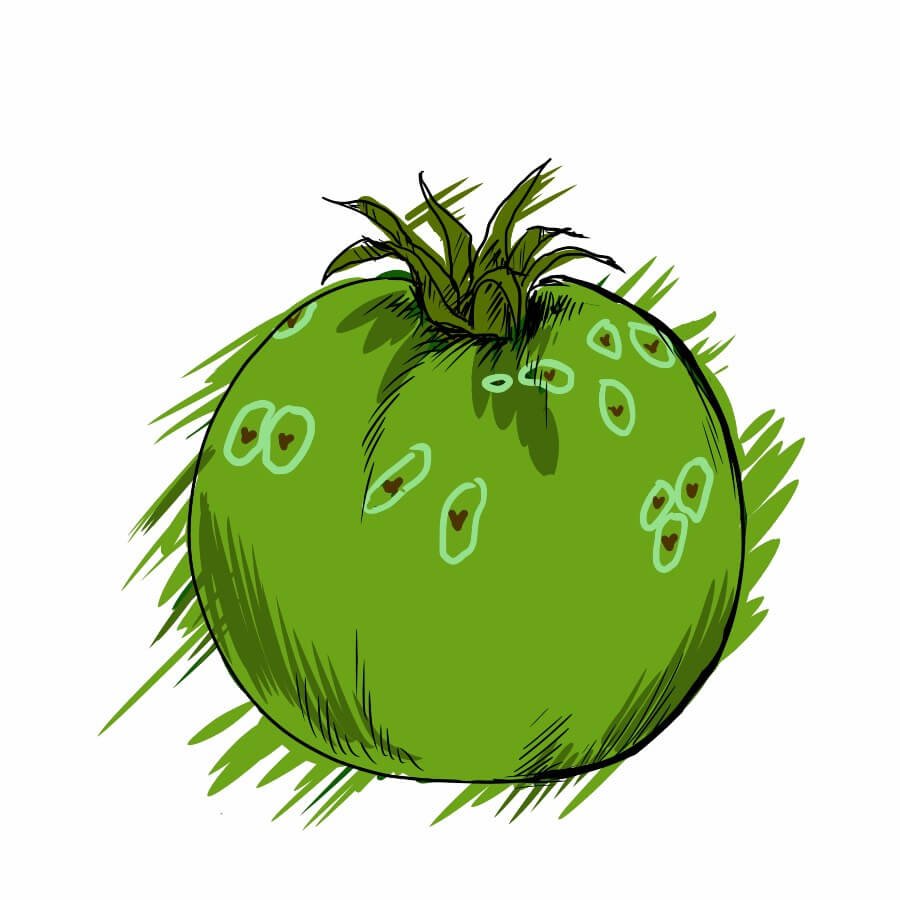
Ghost Spot, also called Botrytis, is a type of fungal disease that affects many different types of plants, including vegetables, fruit trees, flowers, and ornamental plants. The disease gets its name from the pale blotches or “ghostly” spots that appear on the leaves and stems of affected plants.
How does Ghost Spot spread?
Ghost Spot is a highly contagious disease that spreads through spores that are released by infected plants. These spores can be carried by wind, water, or insects and can easily infect other plants in the area. Ghost Spot is most common in cool, damp weather conditions, which are ideal for fungal growth.
What are the symptoms of Ghost Spot?
The most obvious symptom of Ghost Spot is the appearance of white or greyish spots on the leaves and stems of infected plants. These spots may also be surrounded by a brown or yellow ring and will eventually cause the infected part of the plant to wilt and die. In fruit trees, Ghost Spot can cause fruit to rot or become discoloured, making it unsuitable for consumption.
How do you prevent and treat Ghost Spot?
Prevention is the best way to avoid Ghost Spot in your garden. Here are a few tips to keep your plants healthy:
- Water your plants in the morning so that leaves have a chance to dry out during the day.
- Remove infected plant debris as soon as possible, as spores can linger on dead plant material.
- Space plants apart to increase air circulation and decrease humidity.
- Apply a fungicide when necessary, following the manufacturer’s instructions carefully.
If you do notice Ghost Spot in your garden, it’s important to act quickly to avoid the disease spreading. Here are a few steps to take:
- Remove and dispose of infected plant material.
- Avoid watering infected plants from overhead.
- Apply a fungicide to prevent further spread, being sure to follow the instructions carefully.
- Consider pruning your plants to increase air flow and reduce humidity.
- Ghost Spot is a common fungal disease that can affect a wide range of plants, but with careful attention and good gardening practices, it can be prevented and treated effectively.
Ghost Spot FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about Ghost Spot (Botrytis):
Q. What is Ghost Spot (Botrytis)?
A. Ghost Spot, also known as Botrytis, is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including vegetables, fruit trees, flowers, and ornamental plants. It is characterized by the appearance of pale or ghostly spots on the leaves and stems of infected plants.
Q. How does Ghost Spot spread?
A. Ghost Spot spreads through spores that are released by infected plants. These spores can be carried by wind, water, insects, or even on tools and hands. The disease is most prevalent in cool, damp weather conditions, which create an ideal environment for fungal growth.
Q. What are the symptoms of Ghost Spot?
A. The main symptom of Ghost Spot is the presence of white or greyish spots on the leaves and stems of infected plants. These spots may be surrounded by a brown or yellow ring. As the disease progresses, the infected areas can become wilted, necrotic, or discoloured. In fruit trees, Ghost Spot can cause fruits to rot or develop blemishes.
Q. How can I prevent Ghost Spot?
A. To prevent Ghost Spot, it is important to follow good gardening practices:
- Water your plants in the morning to allow leaves to dry out during the day.
- Space plants adequately to improve air circulation and reduce humidity.
- Remove and dispose of any infected plant material promptly.
- Use a fungicide as a preventative measure, especially during periods of high humidity or when Ghost Spot is prevalent in your area.
Q. How can I treat Ghost Spot if my plants are already infected?
A. If you notice Ghost Spot on your plants, take immediate action to prevent the disease from spreading:
- Remove and destroy infected plant material to minimize the chances of spores spreading.
- Avoid overhead watering to prevent further moisture accumulation on plant surfaces.
- Apply a fungicide recommended for Botrytis, following the instructions carefully.
- Consider pruning your plants to improve air circulation and reduce humidity, which will inhibit the growth and spread of the fungus.
Q. Can Ghost Spot be harmful to humans?
A. Ghost Spot is primarily a plant disease and does not pose a significant risk to human health. However, it’s a good practice to avoid direct contact with infected plant material and to wash your hands thoroughly after handling affected plants.